ISO/IEC 15693 is a standard for vicinity cards, which are contactless smart cards that operate at a distance of up to 1 meter from the reader. The protocol defines the communication between the card and the reader, allowing for data exchange and authentication. ISO/IEC 15693 is commonly used in various applications such as access control, identification, and tracking.
Tags Using ISO/IEC 15693
Several types of tags use the ISO/IEC 15693 protocol, including:
- iCode: a type of tag developed by Philips Semiconductors (now NXP)
- Slix: a family of tags from STMicroelectronics
- Slix-L: a low-frequency version of the Slix tag
- Slix-2: an upgraded version of the Slix tag with improved performance and security features
- Other related tags, such as those from EM Microelectronic and Texas Instruments
Difference between ISO/IEC 14443 and ISO/IEC 15693
ISO/IEC 14443 is another standard for contactless smart cards, but it operates at a shorter distance (up to 10 cm) compared to ISO/IEC 15693. The main differences between the two standards are:
- Operating distance: ISO/IEC 15693 has a longer operating distance than ISO/IEC 14443
- Data transfer rate: ISO/IEC 15693 typically has a slower data transfer rate than ISO/IEC 14443
- Applications: ISO/IEC 15693 is often used in applications where a longer read range is required, such as inventory management and supply chain tracking
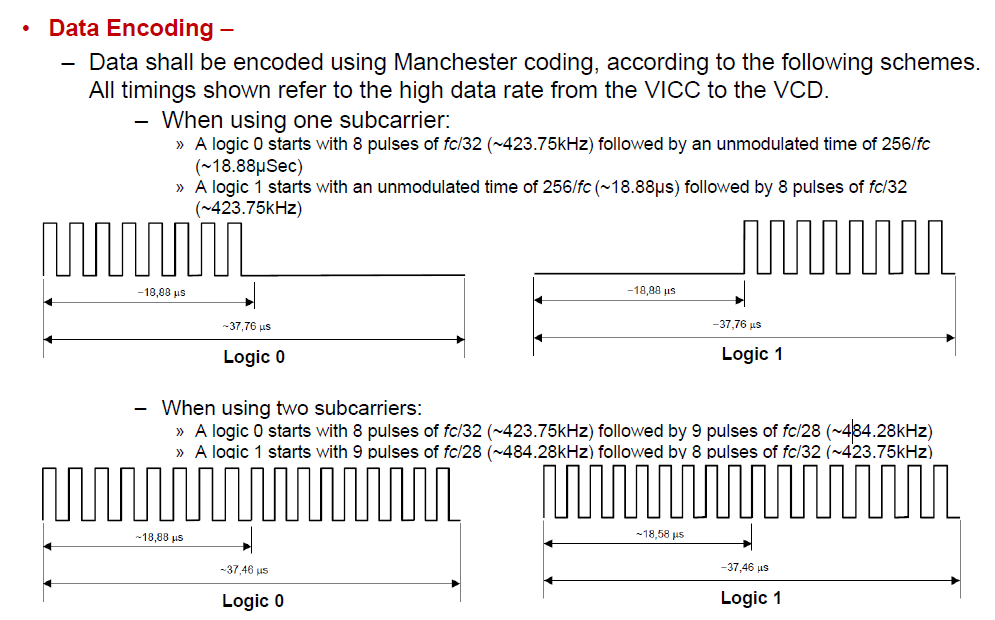
Understanding Subcarrier Modes
ISO/IEC 15693 supports two modes of operation: single subcarrier mode and dual subcarrier mode. The subcarrier frequency is derived from the carrier frequency (fc), which is typically 13.56 MHz.
- Single Subcarrier Mode: When one subcarrier is used, the frequency of the subcarrier load modulation will be fc/32, which is approximately 423.75 kHz. This means that the subcarrier signal will be modulated at a frequency of 423.75 kHz.
- Dual Subcarrier Mode: When two subcarriers are used, the frequencies of the subcarriers are defined as follows:
- f1 (first subcarrier) shall be fc/32, which is approximately 423.75 kHz
- f2 (second subcarrier) shall be fc/28, which is approximately 484.28 kHz
- Additionally, if two subcarriers are present, there shall be a continuous phase relationship between them, ensuring that the subcarriers are synchronized and coherent.
PN532Killer supports dual subcarrier mode out-of-the-box, without requiring any special configuration or setup. This allows users to take full advantage of the ISO/IEC 15693 protocol’s capabilities and ensure reliable communication with tags.
Reading ISO/IEC 15693 Tags with PN532Killer
To read an ISO/IEC 15693 tag using PN532Killer, you can use the PN532 CLI tool. The following commands are available:
hf 15 scan: Scan for ISO15693 tags and print basic informationhf 15 info: Get ISO15693 tag informationhf 15 rdbl: Read block data from ISO15693 taghf 15 wrbl: Write block data to ISO15693 taghf 15 dump: Dump ISO15693 tag datahf 15 raw: Send iso15693 raw command
Emulating ISO/IEC 15693 Tags with PN532Killer
To emulate an ISO/IEC 15693 tag using PN532Killer, you can use the PN532 CLI tool. The following commands are available:
hf 15 gen1uid: Set UID of ISO15693 Emulationhf 15 eSetBlock: Set block data of ISO15693 Emulationhf 15 eSetDump: Set dump data of ISO15693 Emulationhf 15 eSetwriteprotect: Set write protect of ISO15693 Emulationhf 15 eSetResvEasAfiDsfid: Set Resv, EAS, AFI, DSFID of ISO15693 Emulation